If you are planning to launch a start-up, this step-by-step guide will help you through the process.

Starting a business can be a little scary and difficult as it requires a lot of work and planning. You’ll need to research, gather data, plan, and execute necessary pre-launch activities that will help you minimize risks and increase the chances of your business success.
Once launched, you’ll need to work just as hard to keep it growing. You must continuously innovate and think of ways how you can improve your business operations and product offerings.
In this guide, we’ve narrowed down hundreds of different small steps to 10 key steps to help you get your business off the ground and to keep your business venture up and running.
Key Steps to launch a Start-up
1. Start with a great idea
The first step to starting a business is to identify a problem and figure out a solution to solve it. Begin with a great business idea that could fill the needs and gaps of the market you are trying to serve. Be creative, innovative, and think outside the box. Similarly, remember that a great idea doesn’t always have to be a new one. You can improve an existing product or service to better serve the consumer market.
Some of the methods you can use are:
• Improve the product appearance. Product presentation affects consumers’ perception of value and has a significant impact on their choice of what to buy.
• Add a new feature. By adding useful product features and functionality, the company could deliver a more useful product addressing consumer needs and wants. • Identify a new use for a product. It involves repositioning an existing product for a new use or application to change consumers’ perception of it.
One good example is the brand Apple, which started with Steve Jobs’ original idea for a computer. To date, Apple has continuously launched better versions of their existing products, making them more useful and relevant to its target market.
2. Conduct Market Research
You must conduct in-depth market research to better understand your potential customers, how well your product offering fits their needs, and how it compares to your competitors’ offerings. Gather as much data as you can about your target customers -characteristics, behaviour, and pain points.
You should learn about the market trends in your chosen industry to see where your potential start-up might fit in. You can use various methods such as interviews, surveys, focus groups, and industry data analyses.
Important questions that your research should answer are:
• Market demand. What is the demand for some of the desired products or services in your given
market?
• Market size. How many consumers would make up your target and potential market?
• Market saturation. How many competitors are in your market with a similar concept?
• Pricing. How much are customers willing to pay for products and services in your market?
• Consumer engagement. How have similar product or service-based businesses engaged their consumers virtually? Have they moved their sales process online or entered the e-commerce space? Can you replicate that or do it better?
3. Write a Business Plan
Once you have the data you’ve gathered through market research, you may start building your business plan to describe your products and services, your industry, operations, finances, and the market in detail.
Typically, a business plan outlines the first three to five years of your business strategy. It is a written description of your goals and aspirations for the business, what you want to do, and how you plan to do it.
“A business plan is a very important and strategic tool for entrepreneurs. A good business plan not only helps entrepreneurs focus on the specific steps necessary for them to make business ideas succeed, but it also helps them to achieve short-term and long-term objectives.”
-Duquesne University Small Business Development Centre

A properly created business plan gives you a significant competitive advantage. It is also important for getting financing as banks and investors are more likely to give loans or investments to companies that can clearly explain how they’re going to use the money.
A business plan can be as simple or in-depth as you’d like, but most include the following elements:
• Executive summary. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole – what it is, what it does, and why.
• Product description. A section addressing what problem(s) your products or services solve, why it is unique, and how they will be delivered to customers.
• Market analysis and strategy. Describes the company’s primary target audience and where to find this audience.
• Marketing and sales. Covers the specifics of your strategy to market and sell your product offerings to your target consumers.
• Management and organization. Details the business management (list of the owners and executives, as well as key staff members) and organization strategy.
• Operating plan. Part of a business plan that describes how you plan to operate your company -shipping logistics, patents for intellectual property, operations related to personnel, etc.
• Financial plan. Projections include cash flow statements, income statements, and balance sheets. It details how much funding you need and why, and how you plan to pay back any borrowed money.
• Exhibits and appendices. Provides extra information to further support the details outlined in your plan -permits, resumes of company management, marketing materials, legal documents, financial documents, etc.
4. Secure Appropriate Funding
The amount needed to launch a start-up may differ for every business. Raising the right amount of capital funds is essential to keep the business running, enabling it to pay its operational expenses.
Use the financial statements in your business plan to determine how much funding you need to launch successfully. In the process, you may discover that the figures you initially anticipated in the business plan are significantly higher or lower than the actual. Therefore, you have to make the necessary adjustments. To avoid this, you must research and predict realistic financials in your business plan.
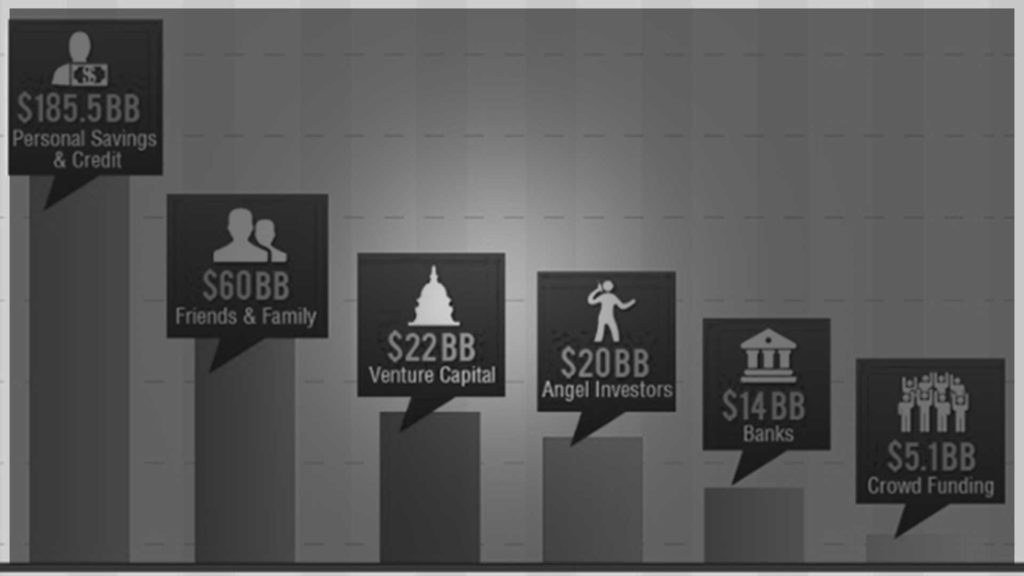
You may consider the following sources of funds to raise the right amount of money needed to launch your start-up:
• Personal Investment. The first investor of your business should be yourself, as it proves to investors and bankers that you have a long-term commitment to your project. This could be in the form of cash or collateral on your asset.
• Love money. Refers to money loaned by a spouse, parents, family, or friends.
• Angel investors. Generally, wealthy individuals or retired company executives who invest directly in small firms.
• Venture capitalists. A type of investor that takes an equity position in the company to help it carry out a promising but high-risk project. VCs are looking for tech-driven businesses in sectors like IT, communications, and biotechnology.
• Crowdfunding. A practice of funding a venture by raising money from a large number of people whom each contribute a relatively small amount.
• Bank loans. The most used source of funding for start-up businesses. Funding from banks typically requires the company to share certain documents like business plan and valuation details along with project reports.
For a start-up business, hiring the entire team often isn’t realistic. You should be resourceful by using your competencies and outsourcing if you can’t afford to recruit.

Additionally, essential business advisors that will help guide you along the way to minimize the risk of starting a business are:
- • Attorneys.
- • Certified Public Accountants (CPAs)
- • Financial advisors
6. Rigorously follow all the legal steps
To get your start-up off the ground, you need to comply with all the legal requirements involved in starting a new business venture.
Some of the business legal requirements that you would need are:
- • Create a Limited Liability Company (LLC) or Corporation. The first legal requirement is to choose that type of business structure for your company and get a business license.
- • Register your business name. Choose a name that reflects your brand and make sure it hasn’t been used.
- • Apply for a federal tax ID number. Also known as Employer Identification Number (EIN) allowing the company to legally hire employees, pay federal taxes, apply for business licenses, and open a business account.
- • Obtain business permits and licenses. Licenses, permits, and fees needed will depend on the business location and primary business activities.
- • Open a business bank account. It is essential to separate your personal and business finances before collecting payments from customers.
To ensure that you have covered all legal and financial standpoints, it is best to consult a lawyer and accountant for professional advice.
7. Establish a location (Physical and Online)
Your business location both physical and online can make or break your business. It is vital to business success as location impacts operating costs and revenue. Likewise, your location of choice affects your brand culture and image to your customers.

Factors to consider when choosing a business location are:
• Customer requirements. Establish a presence where your target market spends their time. For example, businesses such as retail and restaurants could be more saleable in high visibility, high foot traffic areas like main streets.
• Staffing needs. Consider where top talents are residing and work to appeal to your potential employees.
• Sustainability of location. Consider what you need to operate and future expansion plans. For example, you may need storage space or an office for employees.
• Financial matter. For the physical location, you may opt to lease rather than buy a property in the beginning so you can invest your money into other aspects of business -a cheaper alternative to get your start-up in a prime location.
As consumer buying behaviour is moving online, setting up an online presence and e-commerce platform would give the business more advantages. This will improve your brand recognition and potential sale by becoming more visible to a larger audience.
8. Become a marketing expert
It’s not enough that you have a good product, you should have the required marketing skills to communicate and sell your product offering to your targeted audience.
Marketing goes beyond the details of the product offering; it is what will determine a company’s success or failure. The tasks involve working on product-market-fit (PMF) and go-to-market (GTM) strategies, a prerequisite to successful product introduction for a higher chance of market acceptance and growth.
Start-ups may utilise both traditional and digital marketing techniques to sell products and services. The key is finding the right balance between the two main categories of marketing.
Digital Marketing Techniques:
• Content marketing. A form of marketing that focuses on creating, publishing, and distributing content for a targeted audience online.
• Affiliate marketing. A marketing arrangement in which affiliates receive a commission for each visit, signup, or sale they generate for a merchant.
• Email marketing. A direct marketing channel that lets businesses share new products, sales, and updates with customers on their contact lists.
• Search engine optimization (SEO). The process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic to a website or a web page from search engines.
• Social media marketing (SMM). A form of digital marketing that leverages the power of popular social media networks to achieve marketing goals.
• Pay-per-click advertising (PPC). A paid advertisement and promoted search engine results.
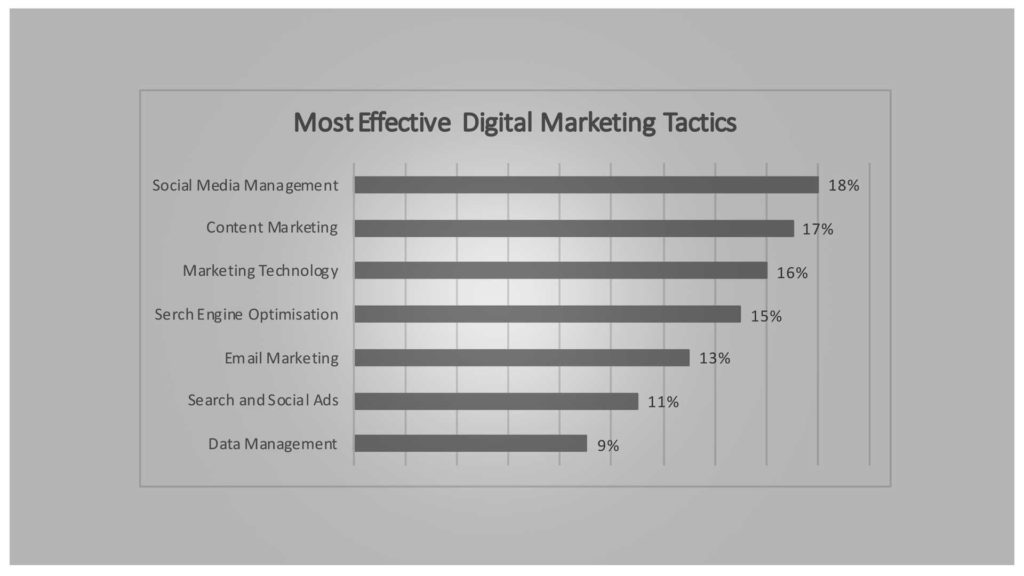
Source: Marketing Resource Effectiveness Survey conducted by Ascend2 and partners I Published 2019
Traditional Marketing Techniques:
• Print advertising. A form of advertising that uses physically printed media like magazines and newspapers.
• Radio advertisements. A type of commercial created for the radio broadcasting medium.
• Television advertisements. A method of marketing used to sell products and services via ads on TV.
• Outdoor Advertising. Refers to the advertisements displayed outside any establishments such as billboards, lamp posts, transit advertising, and outdoor signages.
Marketing needs to be a top priority for start-up companies. This is an important expense that would help the business establish its brand identity, stand out from competition, increase visibility, create customer relationships, and strengthen the company’s reputation.
9. Build a customer base
Having a strong customer base is critical for keeping your business relevant and to guarantee long-term success. To increase your customer base, stay in constant contact with existing and potential customers and continuously innovate and add more value to your product offerings.
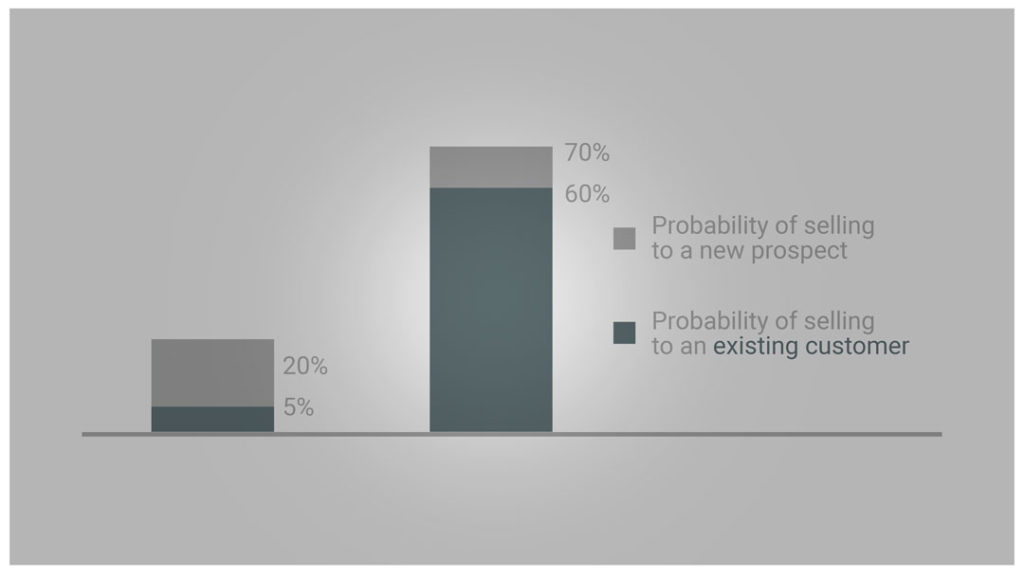
The graph above shows that the probability of selling to existing customers is way higher compared with selling to new prospects. Consequently, establishing, building, and maintaining a customer base will help your start-up get off the ground.
Some techniques that could help you attract and retain customers are:
• Regularly offer great products or services
• Launch loyalty programs
• Use affiliate marketing on social media and other digital marketing platforms
• Keep up and maintain excellent customer support and service
• Regularly conduct market research to keep abreast of the industry and your target audience.
• Ask for feedback directly from the customers
Additionally, the International Council of Shopping Centres (ICSC) research results show that 92% of consumers were loyal to specific retailers because they offered prices that were fair and matched the value of their product, while 79% said it was because of product quality.
10. Plan to change
You can expect drastic changes within the first few years of business operations. In turn, companies need to evolve and adapt their business to the changes in the market and industry.
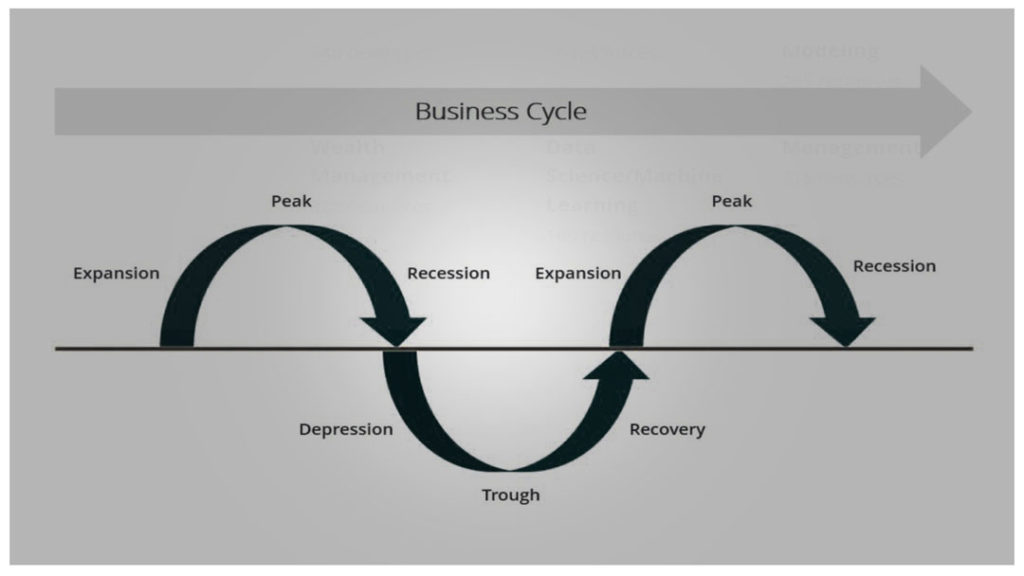
Graphical illustration above indicates that even your business is up and running, it won’t necessarily be smooth sailing for the entire business lifecycle.
Some strategies to make sure you are prepared to adapt are:
• Hire forward-thinker leaders and employees
• Listen to feedback from your stakeholders -customers, suppliers, and others that you work with
• Stay updated on trends in your industry
Final Thoughts
Launching a start-up business won’t be easy. It requires time, effort, money, and many other resources to successfully launch a business. Even if you have a top-notch business idea, if you fail to do the groundwork, it will result in a great chance of business failure. Nevertheless, sometimes, even if you prepare thoroughly, things might certainly go awry, so be prepared to encounter these hurdles and roadblocks along the way.
Don’t lose focus and get discouraged when something goes wrong. Rather, use it as your fuel to keep moving forward and achieve your business objectives and goals. Continuously innovate and adapt to changing business and market situations. It is going to take time, but for sure you will eventually reap the fruits of hard work.


